Contribute to Inkeep Open Source project
Copy page
How to contribute to the Inkeep Agent Framework
Making a Contribution
Thank you for your interest in contributing to the Agent Framework! This document provides guidelines and information for contributors.
Launch the Visual Builder
Prerequisites
Before getting started, ensure you have the following installed on your system:
- Node.js version 22.18 or higher (matches
.node-version) - Docker
- pnpm version 10.10 or higher (matches
packageManager)
Step 1: Clone the repository
Step 2: Run the setup script
For first-time setup, run:
This will:
- Create
.envfrom.env.exampleif missing - Create
~/.inkeep/configfor user-global settings if missing - Add
.envto.gitignoreif needed - Install dependencies
- Start Doltgres (manage) + Postgres (runtime) + SpiceDB (authorization) via
docker-compose.dbs.ymland run migrations
Add API keys for the AI providers you want to use in the root .env or ~/.inkeep/config. ANTHROPIC_API_KEY is required.
Step 3: Run the agent framework
Step 4: Start building!
Open http://localhost:3000 in the browser and start building agents.
Push your project
A key advantage of the Inkeep agent framework is its seamless code-to-visual workflow: define your agents programmatically, push them to the Visual Builder, and continue developing with the intuitive drag-and-drop interface.
Follow the steps below to push your project using the Inkeep CLI.
Step 1: Download the Inkeep CLI
Step 2: Push the project
The CLI reads tenantId and API URLs from the nearest inkeep.config.ts (it searches parent
directories). The cookbook templates default to tenantId: 'default' and agentsApi.url: 'http://localhost:3002'. Update agents-cookbook/template-projects/inkeep.config.ts if needed.
Step 3: Observe the Agent in the Visual Builder
Set up live traces
For full instructions, see Traces. Short version:
- For local SigNoz, clone
agents-optional-local-devand rundocker-compose --profile signoz up -d. - Set
SIGNOZ_URL,SIGNOZ_API_KEY, andOTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_TRACES_ENDPOINTin the root.env(see.env.example). - Restart
pnpm dev, then openhttp://localhost:3080to view traces.
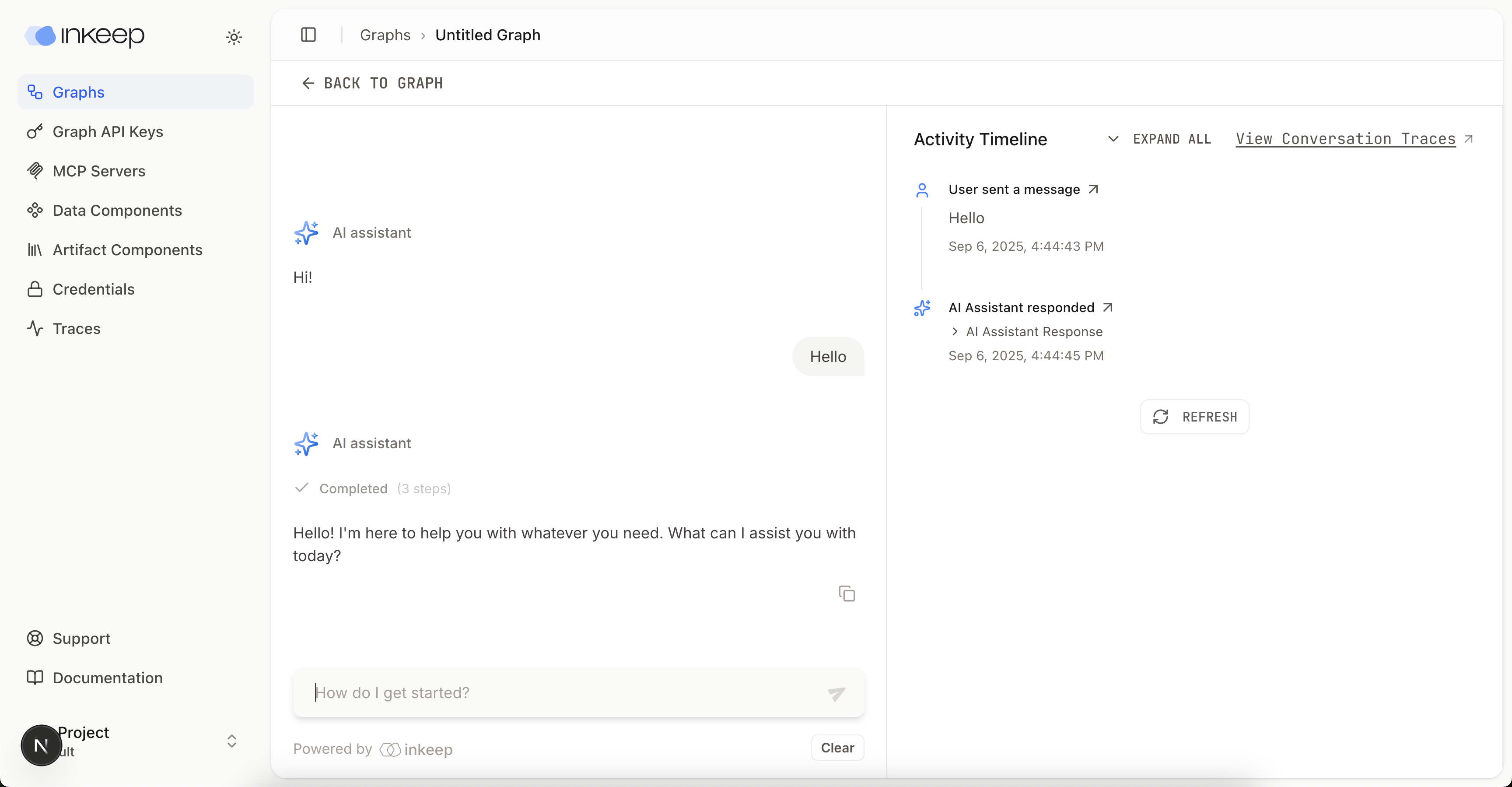
Set up credentials
For Nango setup (cloud or local), follow Use Nango as a credential store. Short version:
- Set
NANGO_SECRET_KEYin the root.env. - For local Nango, start services from
agents-optional-local-dev(docker-compose --profile nango up -d) and setNANGO_SERVER_URL/PUBLIC_NANGO_CONNECT_BASE_URLas needed (see.env.example). - Restart
pnpm dev, then create a credential in the Visual Builder (Credentials tab).
Development Workflow
Git Hooks
This project uses Husky for Git hooks to maintain code quality. The hooks are automatically installed when you run pnpm install.
Pre-commit Hook
The pre-commit hook runs pnpm lint-staged, which:
- Formats and lints staged files with Biome
- Runs
agents-apitests for affected changes
Pre-push Hook
The pre-push hook runs pnpm check:prepush (lint, typecheck, and tests) for all packages except docs and cookbook templates.
Bypassing Checks
While we recommend running all checks, there are legitimate cases where you might need to bypass hooks:
Note: Use these bypass mechanisms sparingly. They're intended for:
- Work-in-progress commits that you'll fix before pushing
- Emergency fixes where speed is critical
- Commits that only touch non-code files (though hooks are smart enough to handle this)
Local checks (CI parity)
pnpm checkruns lint, typecheck, and tests (the same set CI runs).- CI also runs
pnpm format:checkandpnpm knip. - For package-specific commands, see
AGENTS.mdbelow.
CLI Development
Running the CLI Locally
When developing the CLI, you can run the local version directly without global installation:
Testing CLI Changes
- Build the CLI after making changes:
- Test commands locally:
- Run CLI tests:
Switching Between Local and Published CLI
During development, you may need to test both the local development version and the published npm package:
For more CLI setup options, see the CLI docs: https://docs.inkeep.com/guides/cli/overview
Commit Messages
We recommend conventional commit format (not enforced by tooling):
Types:
feat: New featurefix: Bug fixdocs: Documentation changesstyle: Code style changes (formatting, etc.)refactor: Code refactoringtest: Test changeschore: Build process or auxiliary tool changes
Pull Requests
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feat/amazing-feature) - Make your changes
- Ensure
pnpm checkpasses (mirrors CI; see below) - Commit your changes (following commit message guidelines)
- Push to your fork
- Open a pull request
PR Guidelines
- Keep PRs focused on a single feature or fix
- Update tests for any behavior changes
- Update documentation as needed
- Ensure CI passes before requesting review
Continuous Integration
Our CI pipeline runs on all pull requests and includes:
pnpm check(lint, typecheck, tests)pnpm format:checkpnpm knip- Create Agents E2E tests (separate job)
These checks must pass before a PR can be merged. Pre-commit uses lint-staged, pre-push runs pnpm check:prepush, and CI is the source of truth.
AI coding assistants and coding practices
Many of our best coding practices for AI assistants live in AGENTS.md. We render it below for reference.
- Source file: https://github.com/inkeep/agents/blob/main/AGENTS.md
AGENTS.md - Comprehensive Guide for AI Coding Agents
This file provides guidance for AI coding agents (Claude Code, Cursor, Codex, Amp, etc.) when working with code in this repository.
Essential Commands - Quick Reference
Build & Development
- Build:
pnpm build(root) orturbo build - Dev:
pnpm dev(root) or navigate to package and runpnpm dev - Lint:
pnpm lint(check) orpnpm lint:fix(auto-fix) orpnpm check:fix(Biome fix) - Format:
pnpm format(auto) orpnpm format:check(verify) - Typecheck:
pnpm typecheck
Testing
- Test (all):
pnpm testorturbo test - Test (single file):
cd <package> && pnpm test --run <file-path>(use--runto avoid watch mode) - Test (package):
cd <package> && pnpm test --run
Database Operations (run from monorepo root)
- Generate migrations:
pnpm db:generate- Generate Drizzle migrations from schema changes - Apply migrations:
pnpm db:migrate- Apply generated migrations to database - Drop migrations:
pnpm db:drop- Drop migration files (use this to remove migrations, don't manually delete) - Database studio:
pnpm db:studio- Open Drizzle Studio for database inspection - Check schema:
pnpm db:check
Creating Changelog Entries (Changesets)
Create a changeset for any user-facing change to a published package:
Examples:
Valid package names: agents-cli, agents-core, agents-api, agents-manage-ui, agents-sdk, create-agents, ai-sdk-provider
Semver guidance:
- Major: Reserved - do not use without explicit approval
- Minor: Schema changes requiring migration, significant behavior changes
- Patch: Bug fixes, additive features, non-breaking changes
Writing Good Changelog Messages
Target audience: Developers consuming these packages
Style requirements:
- Sentence case: "Add new feature" not "add new feature"
- Start with action verb: Add, Fix, Update, Remove, Improve, Deprecate
- Be specific about what changed and why it matters to consumers
- Keep to 1-2 sentences
Good examples:
- "Fix race condition when multiple agents connect simultaneously"
- "Add
timeoutoption tocreateAgent()for custom connection timeouts" - "Remove deprecated
legacyModeoption (usemode: 'standard'instead)" - "Improve error messages when agent registration fails"
Bad examples:
- "fix bug" (too vague - which bug? what was the impact?)
- "update dependencies" (not user-facing, doesn't need changeset)
- "Refactored the agent connection handler to use async/await" (implementation detail, not user impact)
- "changes" (meaningless)
When NOT to create a changeset:
- Documentation-only changes
- Test-only changes
- Internal tooling/scripts changes
- Changes to ignored packages (agents-ui, agents-docs, cookbook-templates, test-agents)
Multiple changes in one PR: If a PR affects multiple packages independently, create separate changesets for each with specific messages. If changes are tightly coupled (e.g., updating types in core that SDK depends on), use a single changeset listing both packages.
Running Examples / Reference Implementations
- Use
agents-cookbook/for reference implementations and patterns. - There is no
examples/directory; prefer cookbook recipes or package-specific README files.
Documentation Development
Code Style (Biome enforced)
- Imports: Use type imports (
import type { Foo } from './bar'), organize imports enabled, barrel exports (export * from './module') - Formatting: Single quotes, semicolons required, 100 char line width, 2 space indent, ES5 trailing commas
- Types: Explicit types preferred, avoid
anywhere possible (warning), use Zod for validation - Naming: camelCase for variables/functions, PascalCase for types/components, kebab-case for files
- Error Handling: Use try-catch, validate with Zod schemas, handle errors explicitly
- No Comments: Do not add comments unless explicitly requested
Testing (Vitest)
- Place tests in
__tests__/directories adjacent to code - Name:
*.test.tsor*.spec.ts - Pattern:
import { describe, it, expect, beforeEach, vi } from 'vitest' - Run with
--runflag to avoid watch mode - 60-second timeouts for A2A interactions
- Each test worker uses an embedded Postgres (pglite) database with manage/run Drizzle migrations applied in setup
Package Manager
- Always use
pnpm(not npm, yarn, or bun)
Architecture Overview
This is the Inkeep Agent Framework - a multi-agent AI system with A2A (Agent-to-Agent) communication capabilities. The system provides OpenAI Chat Completions compatible API while supporting sophisticated agent orchestration.
Core Components
Unified API (agents-api)
The agents-api package contains all API domains under a single service:
/domains/manage/- Agent configuration, projects, tools, and administrative operations/domains/run/- Agent execution, conversations, A2A communication, and runtime operations/domains/evals/- Evaluation workflows, dataset management, and evaluation triggers
Multi-Agent Framework
Database Schema (PostgreSQL + Drizzle ORM)
- manage-schema.ts - Config tables (Doltgres)
- runtime-schema.ts - Runtime tables (Postgres)
Key Implementation Details
Database Migration Workflow
Standard Workflow
- Edit
packages/agents-core/src/db/manage/manage-schema.tsorpackages/agents-core/src/db/runtime/runtime-schema.ts - Run
pnpm db:generateto create migration files indrizzle/ - (Optional) Make minor edits to the newly generated SQL file if needed due to drizzle-kit limitations
- Run
pnpm db:migrateto apply the migration to the database
Important Rules
- ⚠️ NEVER manually edit files in
drizzle/meta/- these are managed by drizzle-kit - ⚠️ NEVER edit existing migration SQL files after they've been applied - create new migrations instead
- ⚠️ To remove migrations, use
pnpm db:drop- don't manually delete migration files - ✅ Only edit newly generated migrations before first application (if drizzle-kit has limitations)
Testing Patterns (MANDATORY for all new features)
- Vitest: Test framework with 60-second timeouts for A2A interactions
- Isolated Databases: Each test worker gets in-memory SQLite database
- Integration Tests: End-to-end A2A communication testing
- Test Structure: Tests must be in
__tests__directories, named*.test.ts - Coverage Requirements: All new code paths must have test coverage
Example Test Structure
Environment Configuration
Required environment variables in .env files:
High Product-level Thinking
This repo is a product with multiple user-facing surfaces and shared contracts. A “small” change in one place can have real side effects elsewhere.
Rule: Do NOT implement additional work beyond what the user requested. If you identify likely cross-surface impacts, flag them and ask the user to get full clarity and ensure high degree of product-level thinking. You can flag prior to starting new work/tasks, but also if you identify ambiguities or additional things to consider mid-execution.
If the request is NOT backed by a PRD, a well-specced artifact, or clearly scoped small task, pause and ask targeted, highly relevant questions when the blast radius is unclear. When applicable, suggest user make a PRD; offer to help by leveraging the prd skill.
Your goal is to AVOID:
- locking in unintended behavior
- making changes without thinking through all potential interaction points for how a user may consume or interact with a product change
- breaking changes or breaking data contracts without clear acknowledgement and plan
- missing critical dimensions to feautre development relevant, like authorization or security
- identify any side effects of the work that is being asked
- implementations that contradict or duplicate existing patterns/abstractions
Your responsibility is to think through the work that is being done from all dimensions and considerations.
What to clarify (high-signal triggers)
- Definition shapes / shared types / validation rules (agent/project/tool/credential/etc.)
- Runtime behavior or streaming formats (responses, tool calls, artifacts/components)
- Tracing / telemetry (span names, attribute keys, correlation IDs, exporter config)
- Resources, endpoints, or actions (create/update/delete, new capabilities)
- Auth / permissions / tenancy (view/use/edit boundaries, RBAC, fine-grained authz, multi-tenant scoping)
Surface area analysis (load before planning or implementing)
This product has 50+ customer-facing and 100+ internal tooling/devops surfaces with complex dependency chains. When planning or implementing any feature or change, load the relevant surface area skill to map the blast radius and plan "to-dos" of all areas that need to be addressed before writing a line of code:
| Skill | Scope | Load when |
|---|---|---|
product-surface-areas | APIs, SDKs, CLI, UIs, Widgets, Event Streams, docs, protocols, templates, etc. | Change affects anything a customer (developer or no-code admin) uses or depends on |
internal-surface-areas | Build, CI/CD, DB, auth, runtime engine, test infra, internal AI tooling, etc. | Change affects infrastructure, tooling, or shared internals |
Tip: Both skills include dependency graphs, breaking change impact matrices, and transitive chain tracing for systematically identifying relevant surfaces and code paths that may be affected by changes.
Development Guidelines
⚠️ MANDATORY: Required for All New Features
ALL new work MUST include these three components - NO EXCEPTIONS:
✅ 1. Unit Tests
- Write comprehensive unit tests using Vitest
- Place tests in
__tests__directories adjacent to the code - Follow naming convention:
*.test.ts - Minimum coverage for new code paths
- Test both success and error cases
✅ 2. Agent Builder UI Components
- Add corresponding UI components in
/agents-manage-ui/src/components/ - Include form validation schemas
- Update relevant pages in
/agents-manage-ui/src/app/ - Follow existing Next.js and React patterns
- Use the existing UI component library
✅ 3. Documentation
- Create or update documentation in
/agents-docs/content/docs/(public-facing docs) - Documentation should be in MDX format (
.mdxfiles) - Follow the write-docs skill whenever creating or modifying documentation
Before marking any feature complete, verify:
- Tests written and passing (
pnpm test) - UI components implemented in agents-manage-ui
- Documentation added to
/agents-docs/ - All linting passes (
pnpm lint) - Code is formatted (
pnpm formatto auto-fix,pnpm format:checkto verify) - Surface area and breaking changes have been addressed as agreed with the user (see “Clarify scope and surface area before implementing”).
📋 Standard Development Workflow
After completing a feature and ensuring all tests, typecheck, and build are passing:
-
Create a new branch (if not already on one):
-
Run verification commands to ensure everything passes:
-
Commit your changes with a descriptive message
-
Open a GitHub Pull Request once all checks pass:
This is the standard development procedure to ensure code review and CI/CD processes.
Note: The user may override this workflow if they prefer to work directly on main or have different branch strategies.
📁 Git Worktrees for Parallel Feature Development
Git worktrees allow you to work on multiple features simultaneously without switching branches in your main working directory. This is especially useful when you need to quickly switch context between different Linear tickets or have multiple features in progress.
Creating a Worktree
To spin off a new scope of work in a separate directory using git worktrees:
Important Conventions:
- The directory name and branch name should match (e.g.,
pull-instrumentmatchesfeat/pull-instrument) - Branch names should reference a Linear ticket when applicable (e.g.,
feat/ENG-123-feature-name) - Worktree directories are temporary and should be removed after the work is complete
Working with Worktrees
When to Use Worktrees
✅ Use worktrees when:
- Working on multiple features simultaneously
- Need to quickly test/review another branch without stashing current work
- Running long-running processes (tests, builds) while working on something else
- Comparing implementations across different branches side-by-side
❌ Use regular branches when:
- Working on a single feature at a time
- Making quick hotfixes or small changes
- The overhead of managing multiple directories isn't worth it
Reference: git-worktree documentation
When Working with Agents
- Always call
graph.init()after creating agent relationships to persist to database - Use builder patterns (
agent(),subAgent(),tool()) instead of direct database manipulation - Preserve contextId when implementing transfer/delegation logic - extract from task IDs if needed
- Validate tool results with proper type guards instead of unsafe casting
- Test A2A communication end-to-end when adding new agent relationships
- Follow the mandatory requirements above for all new features
Performance Considerations
- Parallelize database operations using
Promise.all()instead of sequentialawaitcalls - Optimize array processing with
flatMap()andfilter()instead of nested loops - Implement cleanup mechanisms for debug files and logs to prevent memory leaks
Internal Self-Calls: getInProcessFetch() vs fetch
Any code in agents-api that makes internal A2A calls or self-referencing API calls (i.e. calling another route on the same service) MUST use getInProcessFetch() from agents-api/src/utils/in-process-fetch.ts instead of the global fetch.
getInProcessFetch()routes the request through the Hono app's middleware stack in-process, guaranteeing it stays on the same instance.- Global
fetchsends the request over the network, where a load balancer may route it to a different instance — breaking features that depend on process-local state (e.g. the stream helper registry for SSE streaming). - This bug only manifests under load in multi-instance deployments and is extremely difficult to diagnose.
When to use:
| Scenario | Use |
|---|---|
| Internal A2A delegation/transfer (same service) | getInProcessFetch() |
| Eval service calling the chat API on itself | getInProcessFetch() |
| Forwarding requests to internal workflow routes | getInProcessFetch() |
| Calling an external service or third-party API | Global fetch |
| Test environments (falls back automatically) | Either (auto-fallback) |
Common Gotchas
- Empty Task Messages: Ensure task messages contain actual text content
- Context Extraction: For delegation scenarios, extract contextId from task ID patterns like
task_math-demo-123456-chatcmpl-789 - Tool Health: MCP tools require health checks before use
- Agent Discovery: Agents register capabilities via
/.well-known/{subAgentId}/agent.jsonendpoints
File Locations
- API Domains:
agents-api/src/domains/(unified API with manage/, run/, evals/ domains) - Core Agents:
agents-api/src/domains/run/agents/Agent.ts,agents-api/src/domains/run/agents/generateTaskHandler.ts - A2A Communication:
agents-api/src/domains/run/a2a/,agents-api/src/domains/run/handlers/executionHandler.ts - Evaluations:
agents-api/src/domains/evals/(evaluation workflows, dataset runs, triggers) - Management Routes:
agents-api/src/domains/manage/routes/(agent config, projects, tools, credentials) - Database Layer:
packages/agents-core/src/data-access/(agents, tasks, conversations, tools) - Builder Patterns:
packages/agents-sdk/src/(agent.ts, subAgent.ts, tool.ts, project.ts) - Schemas:
packages/agents-core/src/db/manage/manage-schema.ts,packages/agents-core/src/db/runtime/runtime-schema.ts(Drizzle),packages/agents-core/src/validation/(Zod validation) - Tests:
agents-api/src/__tests__/(unit and integration tests) - UI Components:
agents-manage-ui/src/components/(React components) - UI Pages:
agents-manage-ui/src/app/(Next.js pages and routing) - Documentation:
agents-docs/(Next.js/Fumadocs public documentation site) - Legacy Documentation:
docs-legacy/(internal/development notes) - Examples:
agents-cookbook/for reference implementations
Feature Development Examples
Example: Adding a New Feature
1. Unit Test Example
2. Agent Builder UI Component Example
3. Documentation Example
API Reference
NewFeature(config)- Creates a new feature instanceexecute()- Executes the featurevalidate()- Validates configuration
Examples
[Include practical examples here]
Common Debugging Workflows
Debugging Agent Transfers:
- View traces:
curl "http://localhost:16686/api/traces?service=inkeep-agents-api&tags=%7B%22conversation.id%22:%22conv-123%22%7D"
Debugging Tool Calls:
- Find tool call traces:
curl "http://localhost:16686/api/traces?service=inkeep-agents-api&operation=tool.call&limit=10"
Debugging Task Delegation:
- Trace execution flow:
curl "http://localhost:16686/api/traces?service=inkeep-agents-api&tags=%7B%22task.id%22:%22task-id%22%7D"
Debugging Performance Issues:
- Find slow operations:
curl "http://localhost:16686/api/traces?service=inkeep-agents-api&minDuration=5s" - View error traces:
curl "http://localhost:16686/api/traces?service=inkeep-agents-api&tags=%7B%22error%22:%22true%22%7D"
AI Coding Assistant Guidance
This repository uses symlinks so multiple AI tools (Claude Code, Cursor, Codex) read from the same instructions.
| Source (edit this) | Symlinks (don't edit) |
|---|---|
AGENTS.md | CLAUDE.md |
.cursor/skills/ | .claude/skills/, .codex/skills/ |
AGENTS.md is always loaded by the Agent Harness, and Skills provide on-demand expertise for specific development tasks. They are auto-discovered — no need to document them here.
Human-only workflows (process, PR etiquette, roadmap context) belong in this guide and the broader contributing docs above.
Questions?
If you have questions about contributing, please:
- Check existing issues and discussions
- Open a new issue if your question isn't addressed
- Reach out to the maintainers
Thank you for contributing!